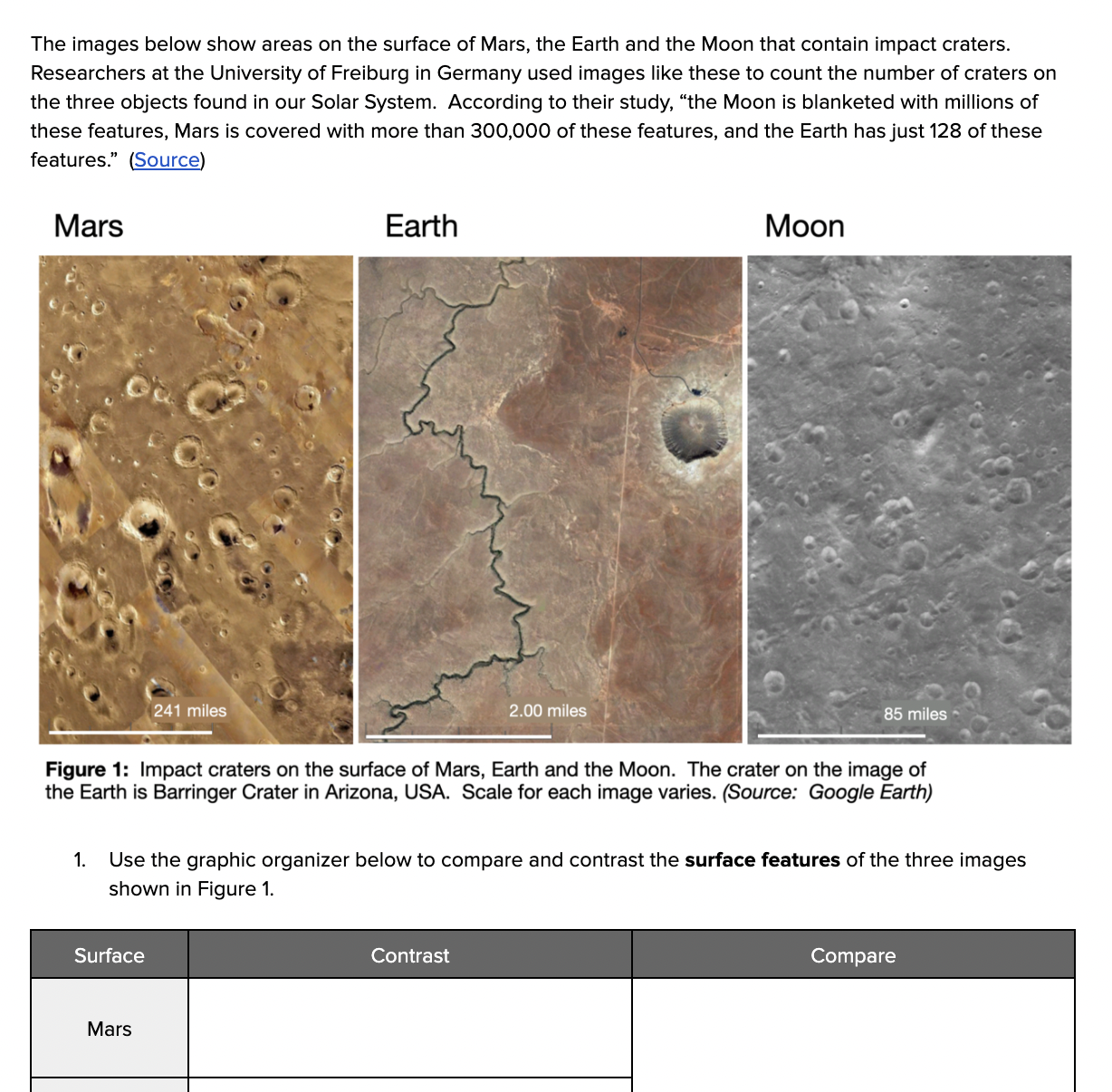
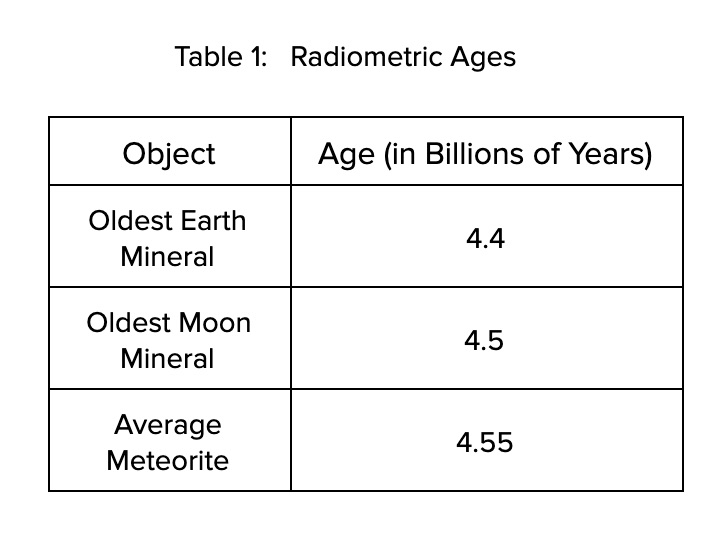
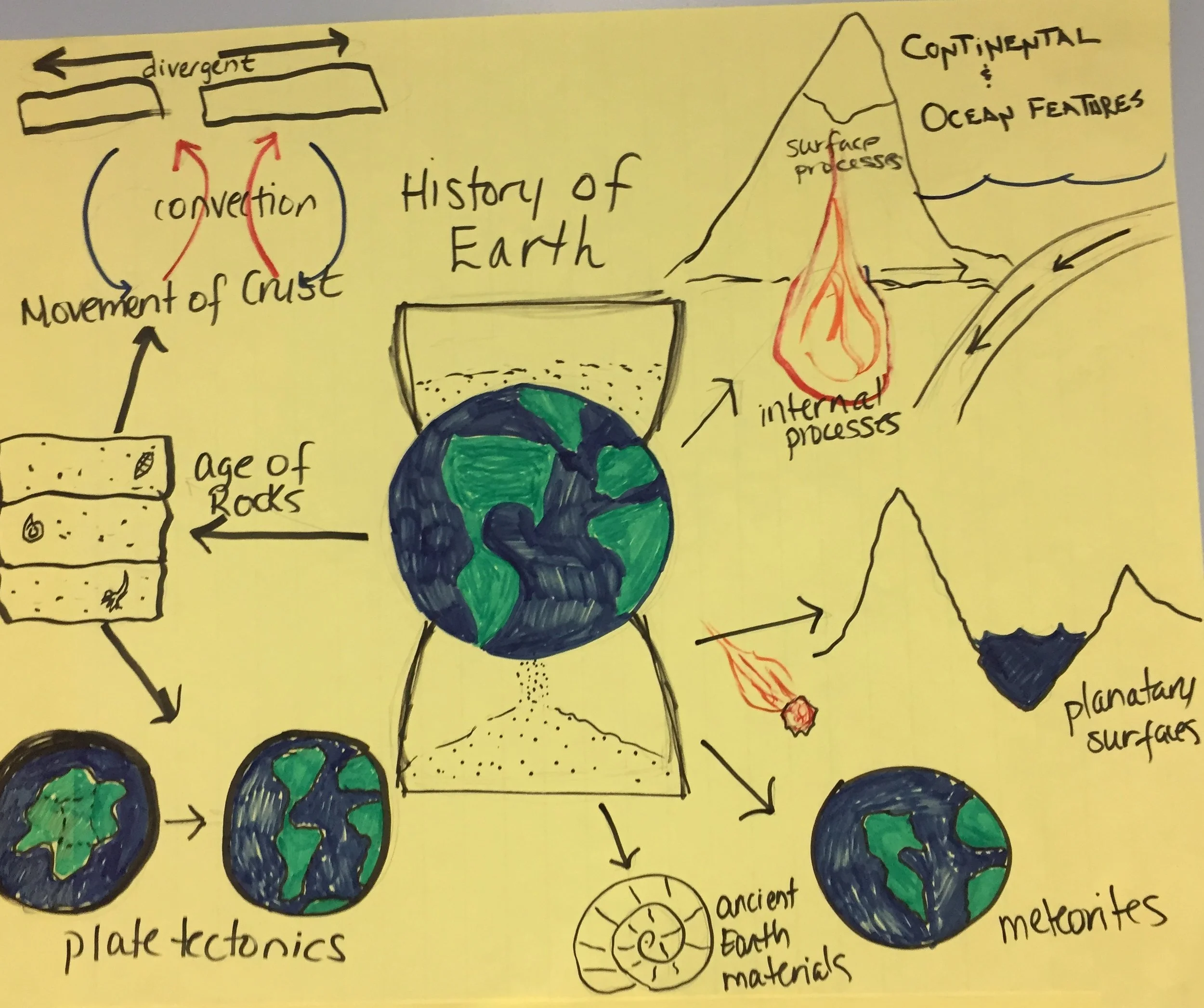
HS-ESS1-6: Evidence of the Earth's History
Apply scientific reasoning and evidence from ancient earth materials, meteorites, and other planetary surfaces to construct an account of earth’s formation and early history. (Stability and Change)
Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on using available evidence within the solar system to reconstruct the early history of Earth, which formed along with the rest of the solar system 4.6 billion years ago. Examples of evidence include the absolute ages of ancient materials (obtained by radiometric dating of meteorites, moon rocks, and Earth’s oldest minerals), the sizes and compositions of solar system objects, and the impact cratering record of planetary surfaces.
Assessment Boundary: none
Science Practices
Constructing Explanations
Disciplinary Core Ideas
PS1.C: Nuclear Processes
ESS1.C: The History of Planet Earth
Crosscutting Concepts
Stability and Change
Assessments
The Wonder of Science Assessments
Shared Assessments
The following assessments were shared by teachers implementing the NGSS. Many of these are drafts and should be used accordingly. Feel free to improve these assessments or contribute your own. Learn more here.
Instructional Resources
Mini Lessons
The Wonder of Science Resources
Anchor Charts
Phenomena
Videos
Learning Plans
Storylines
Common Core Connections
ELA/Literacy
RST.11-12.1 - Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to important distinctions the author makes and to any gaps or inconsistencies in the account.
RST.11-12.8 - Evaluate the hypotheses, data, analysis, and conclusions in a science or technical text, verifying the data when possible and corroborating or challenging conclusions with other sources of information.
WHST.9-12.1 - Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content.
Mathematics
HSF-IF.B.5 - Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship it describes.
HSN-Q.A.1 - Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multi-step problems; choose and interpret units consistently in formulas; choose and interpret the scale and the origin in graphs and data displays.
HSN-Q.A.2 - Define appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptive modeling.
HSN-Q.A.3 - Choose a level of accuracy appropriate to limitations on measurement when reporting quantities.
HSS-ID.B.6 - Represent data on two quantitative variables on a scatter plot, and describe how the variables are related.
MP.2 - Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
*Next Generation Science Standards is a registered trademark of Achieve. Neither Achieve nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it. Visit the official NGSS website.