MS-ESS2-5: Interacting Air Masses and Weather
Collect data to provide evidence for how the motions and complex interactions of air masses results in changes in weather conditions. (Cause and Effect)
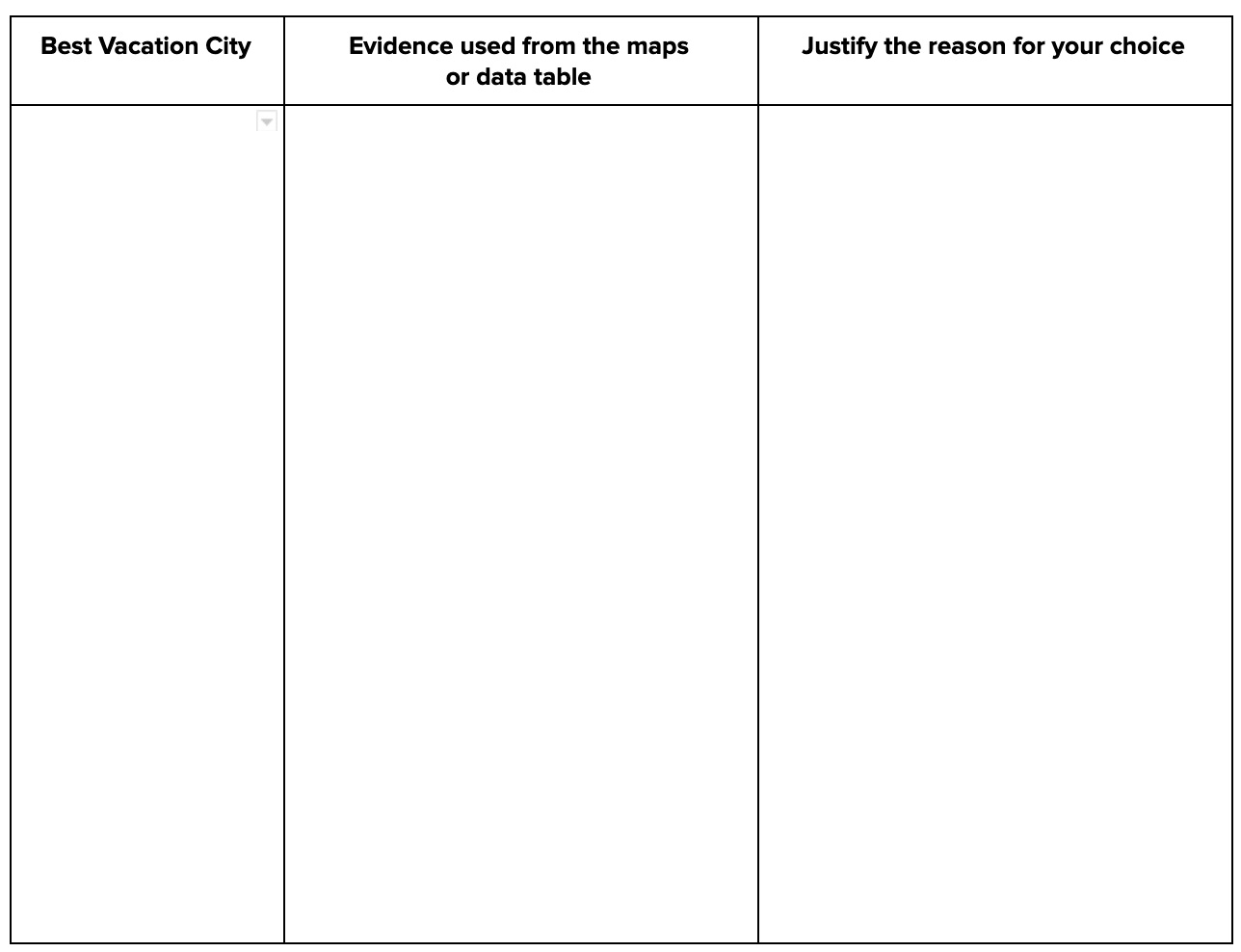
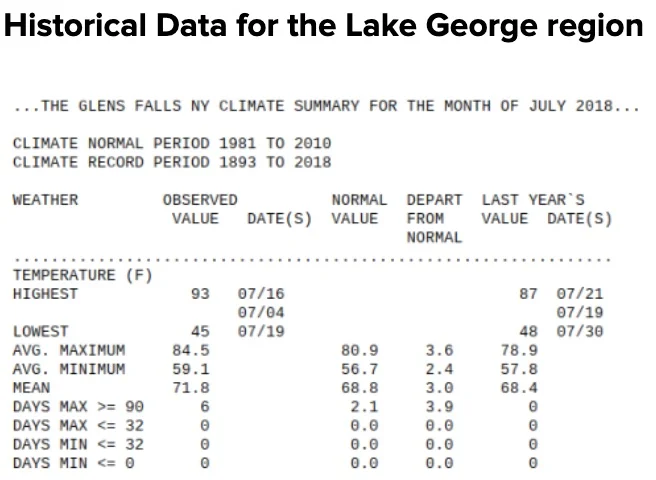
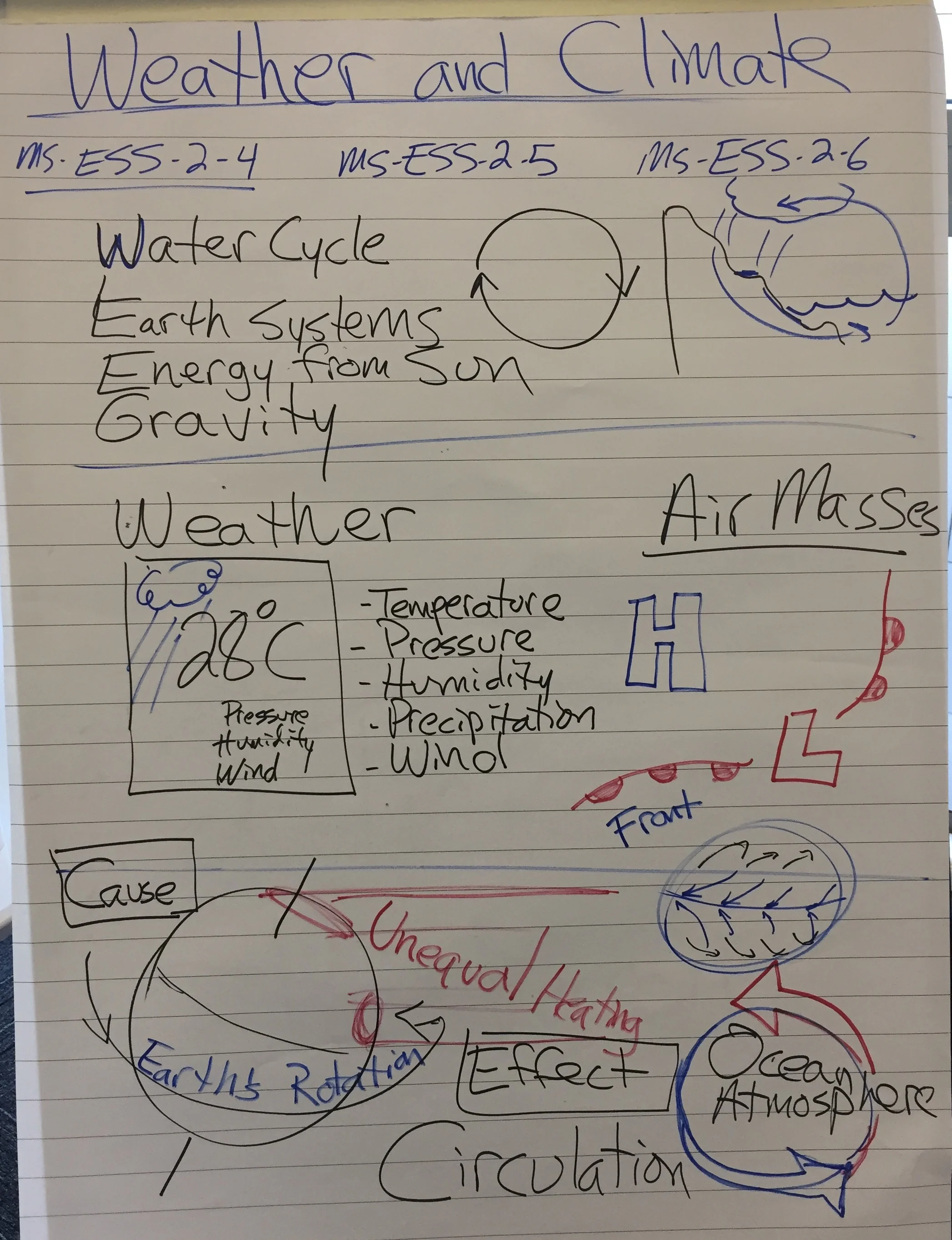
Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on how air masses flow from regions of high pressure to low pressure, causing weather (defined by temperature, pressure, humidity, precipitation, and wind) at a fixed location to change over time, and how sudden changes in weather can result when different air masses collide. Emphasis is on how weather can be predicted within probabilistic ranges. Examples of data can be provided to students (such as weather maps, diagrams, and visualizations) or obtained through laboratory experiments (such as with condensation).
Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include recalling the names of cloud types or weather symbols used on weather maps or the reported diagrams from weather stations.
Science Practices
Planning and Carrying Out Investigations
Disciplinary Core Ideas
ESS2.C: The Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes
ESS2.D: Weather and Climate
Crosscutting Concepts
Cause and Effect
Assessments
The Wonder of Science Assessments
Shared Assessments
The following assessments were shared by teachers implementing the NGSS. Many of these are drafts and should be used accordingly. Feel free to improve these assessments or contribute your own. Learn more here.
Instructional Resources
Mini Lessons
The Wonder of Science Resources
Anchor Charts
Phenomena
Videos
Learning Plans
Storylines
Common Core Connections
ELA/Literacy
RST.6-8.1 - Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts.
RST.6-8.9 - Compare and contrast the information gained from experiments, simulations, video, or multimedia sources with that gained from reading a text on the same topic.
WHST.6-8.8 - Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources, using search terms effectively; assess the credibility and accuracy of each source; and quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions of others while avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation.
Mathematics
6.NS.C.5 - Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation.
MP.2 - Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
*Next Generation Science Standards is a registered trademark of Achieve. Neither Achieve nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it. Visit the official NGSS website.