MS-ESS2-6: Atmospheric and Oceanic Circulation
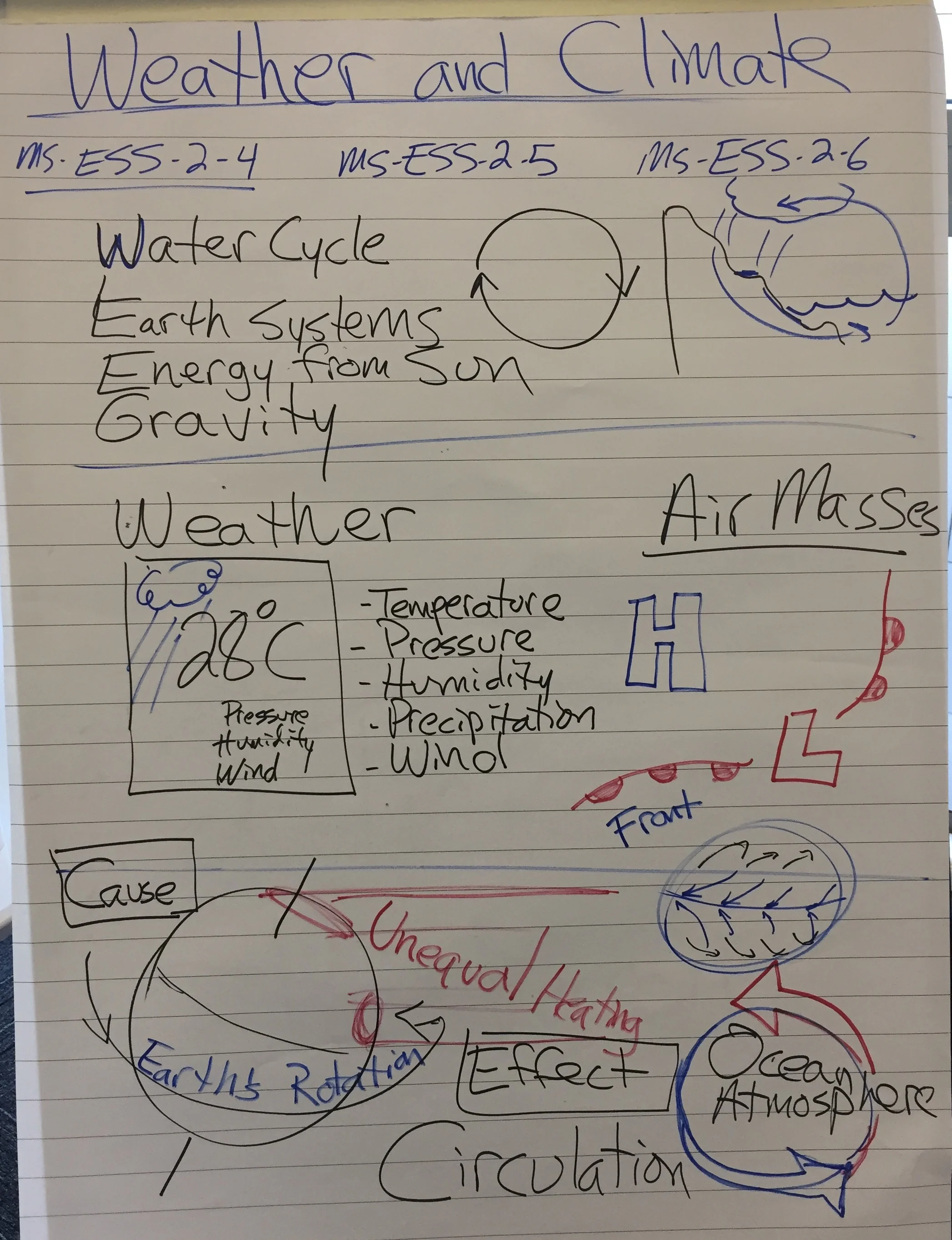
Develop and use a model to describe how unequal heating and rotation of the earth cause patterns of atmospheric and oceanic circulation that determine regional climates. (Systems and System Models)
Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on how patterns vary by latitude, altitude, and geographic land distribution. Emphasis of atmospheric circulation is on the sunlight-driven latitudinal banding, the Coriolis effect, and resulting prevailing winds; emphasis of ocean circulation is on the transfer of heat by the global ocean convection cycle, which is constrained by the Coriolis effect and the outlines of continents. Examples of models can be diagrams, maps and globes, or digital representations
Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the dynamics of the Coriolis effect.
Science Practices
Developing and Using Models
Disciplinary Core Ideas
ESS2.C: The Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes
ESS2.D: Weather and Climate
Crosscutting Concepts
Systems and System Models
Assessments
The Wonder of Science Assessments
Shared Assessments
The following assessments were shared by teachers implementing the NGSS. Many of these are drafts and should be used accordingly. Feel free to improve these assessments or contribute your own. Learn more here.
Instructional Resources
Mini Lessons
The Wonder of Science Resources
Anchor Charts
Phenomena
Videos
Learning Plans
Storylines
Common Core Connections
ELA/Literacy
SL.8.5 - Integrate multimedia and visual displays into presentations to clarify information, strengthen claims and evidence, and add interest.
*Next Generation Science Standards is a registered trademark of Achieve. Neither Achieve nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it. Visit the official NGSS website.