MS-ESS3-3: Human Impact on the Environment
Apply scientific principles to design a method for monitoring and minimizing a human impact on the environment. (Cause and Effect)
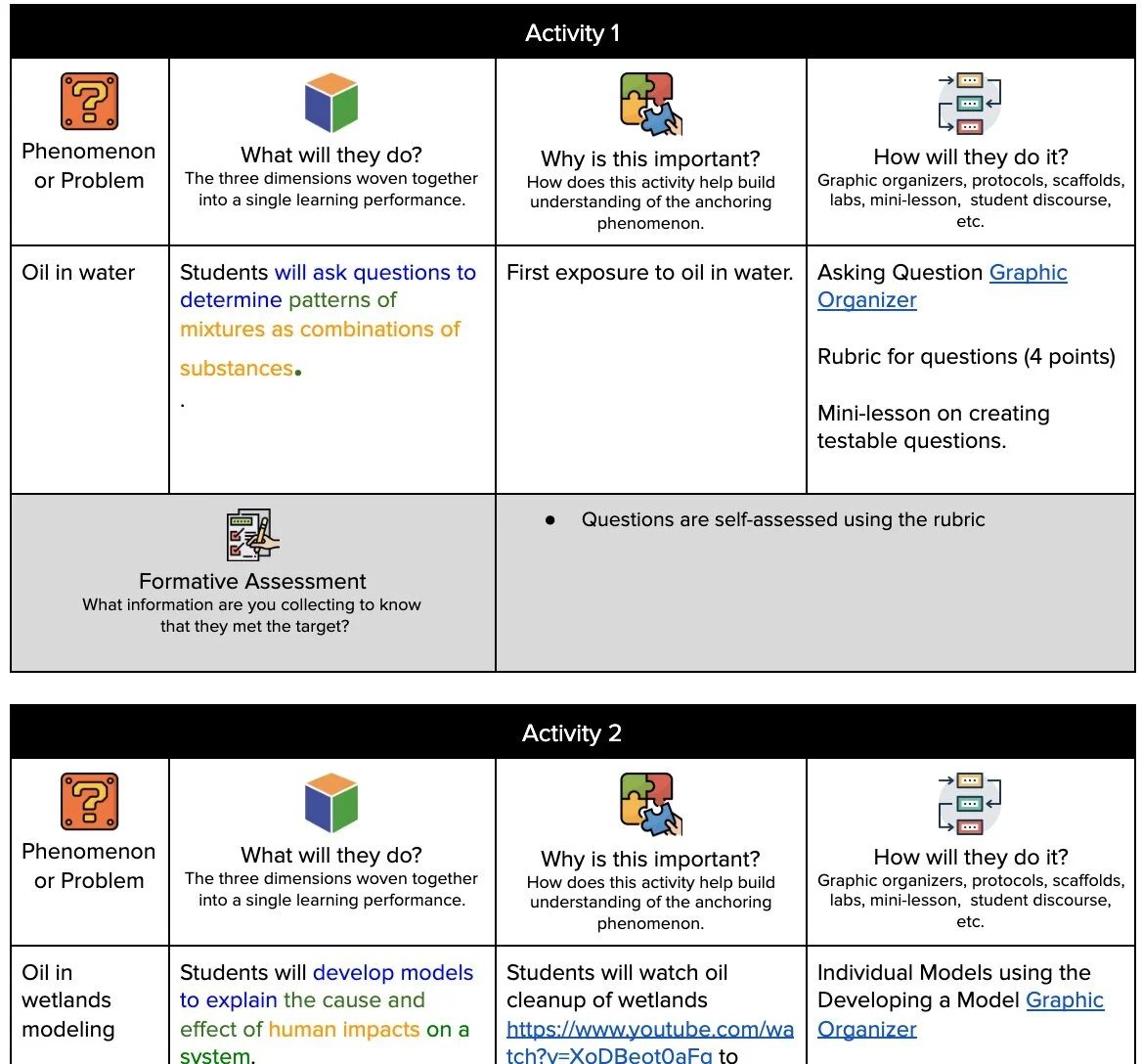
Clarification Statement: Examples of the design process include examining human environmental impacts, assessing the kinds of solutions that are feasible, and designing and evaluating solutions that could reduce that impact. Examples of human impacts can include water usage (such as the withdrawal of water from streams and aquifers or the construction of dams and levees), land usage (such as urban development, agriculture, or the removal of wetlands), and pollution (such as of the air, water, or land).
Assessment Boundary: none
Science Practices
Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions
Disciplinary Core Ideas
ESS3.C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
Crosscutting Concepts
Cause and Effect
Assessments
The Wonder of Science Assessments
Shared Assessments
The following assessments were shared by teachers implementing the NGSS. Many of these are drafts and should be used accordingly. Feel free to improve these assessments or contribute your own. Learn more here.
Instructional Resources
Mini Lessons
The Wonder of Science Resources
Anchor Charts
Phenomena
Videos
Learning Plans
Storylines
Common Core Connections
ELA/Literacy
WHST.6-8.7 - Conduct short research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question), drawing on several sources and generating additional related, focused questions that allow for multiple avenues of exploration.
WHST.6-8.8 - Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources, using search terms effectively; assess the credibility and accuracy of each source; and quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions of others while avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation.
WHST.6-8.9 - Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis reflection, and research.
Mathematics
6.EE.B.6 - Use variables to represent numbers and write expressions when solving a real-world or mathematical problem; understand that a variable can represent an unknown number, or, depending on the purpose at hand, any number in a specified set.
6.RP.A.1 - Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities.
7.EE.B.4 - Use variables to represent quantities in a real-world or mathematical problem, and construct simple equations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoning about the quantities.
7.RP.A.2 - Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities.
*Next Generation Science Standards is a registered trademark of Achieve. Neither Achieve nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it. Visit the official NGSS website.