LS4.A: Evidence of Common Ancestry and Diversity
In this video Paul Andersen describes several types of evidence for common ancestry. This evidence is contained in the fossils, embryos and molecules of living organisms. Even though life on our planet is incredibly diverse there are common threads that run through everything. This idea was most elegantly put forward by Charles Darwin before much of this evidence was gathered. A teaching progression K-12 is also included.
LS3.B: Variation of Traits
In this video Paul Andersen explains how variation is created in a population over time. Variation in offspring is caused by genetic recombination, mutations and environmental effects. Parental DNA is recombined using the process of meiosis. Mutations can add novel genes to a population and the environment can shape the expression of genes. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.
LS3.A: Inheritance of Traits
In this video Paul Andersen explains the importance of DNA is organisms. DNA contains the blueprint for each organisms. The DNA codes for the mRNA which creates proteins. The DNA also is the unit of inheritance which is passed from generation to generation. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.
LS2.D: Social Interactions and Group Behavior
In this video Paul Andersen explains the importance of social interactions and group behavior. Organisms live in groups because it overs them greater success and has been selected for through natural selection. Some groups are stable and some are fluid. Some groups show an established hierarchy and some do not. A K-12 teaching progress is included.
LS2.C: Ecosystem Dynamics, Functioning, and Resilience
In this video Paul Andersen explains how ecosystems respond to disruptions. Disruptions can cause changes in the number and variety of organisms. It can also lead to migration, extinction or even speciation. Ecosystems that have a higher biodiversity are able to respond to large disruptions over time. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.
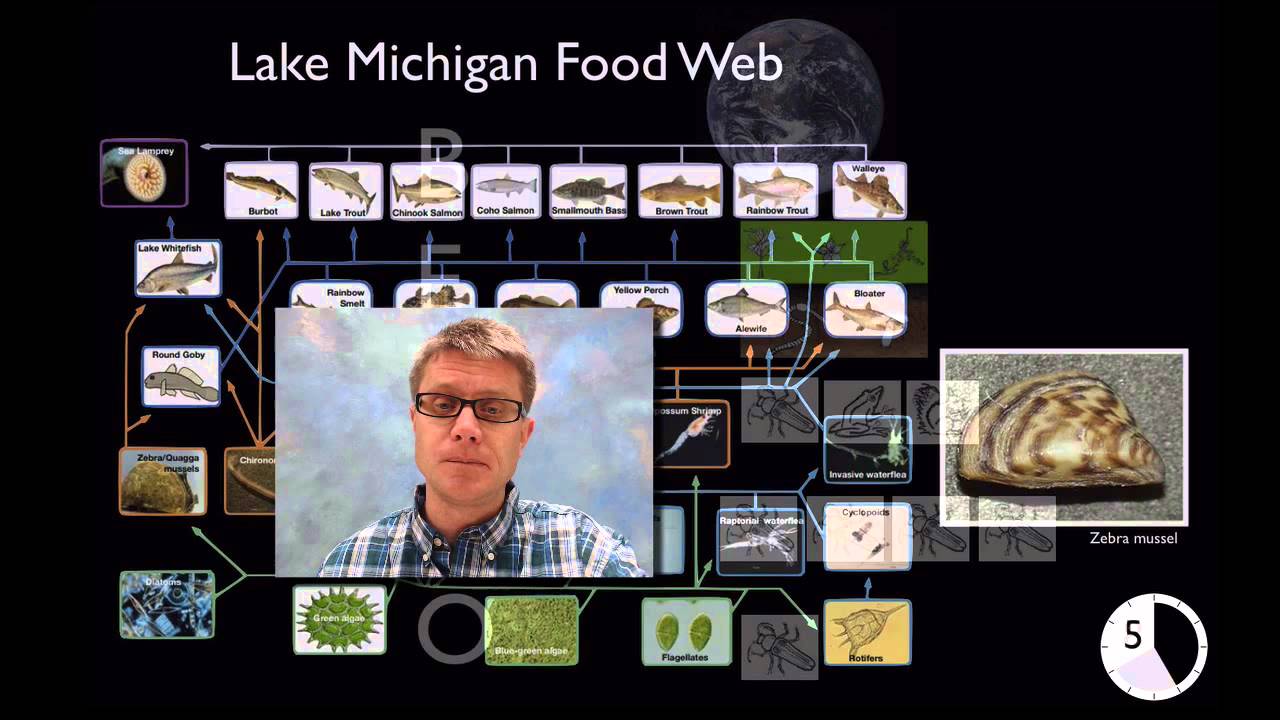
LS2.B: Cycle of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems
In this video Paul Andersen explains how matter moves from the environment into living organisms and back into the environment. Food webs are used to show how matter and energy move through organisms. Ecological pyramids show that matter and energy are lost as they move from producers to consumers.
LS2.A: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems
In this video Paul Andersen explains the important relationships that exist in ecosystems. He starts by delineating between organisms and their environment. He explains how food webs can be used to show energy and matter flow in a community. He describes the levels studied within ecology and explains how population interact at the level of a community. He finishes be describing population growth and carrying capacity.
LS1.D: Information Processing
In this video Paul Andersen explains how information is processed in in animals. He starts by describing the different forms of information and how they are received by receptors. He explains how information is received by the brain and processed using different regions. He finishes with a description of memories and emotions.
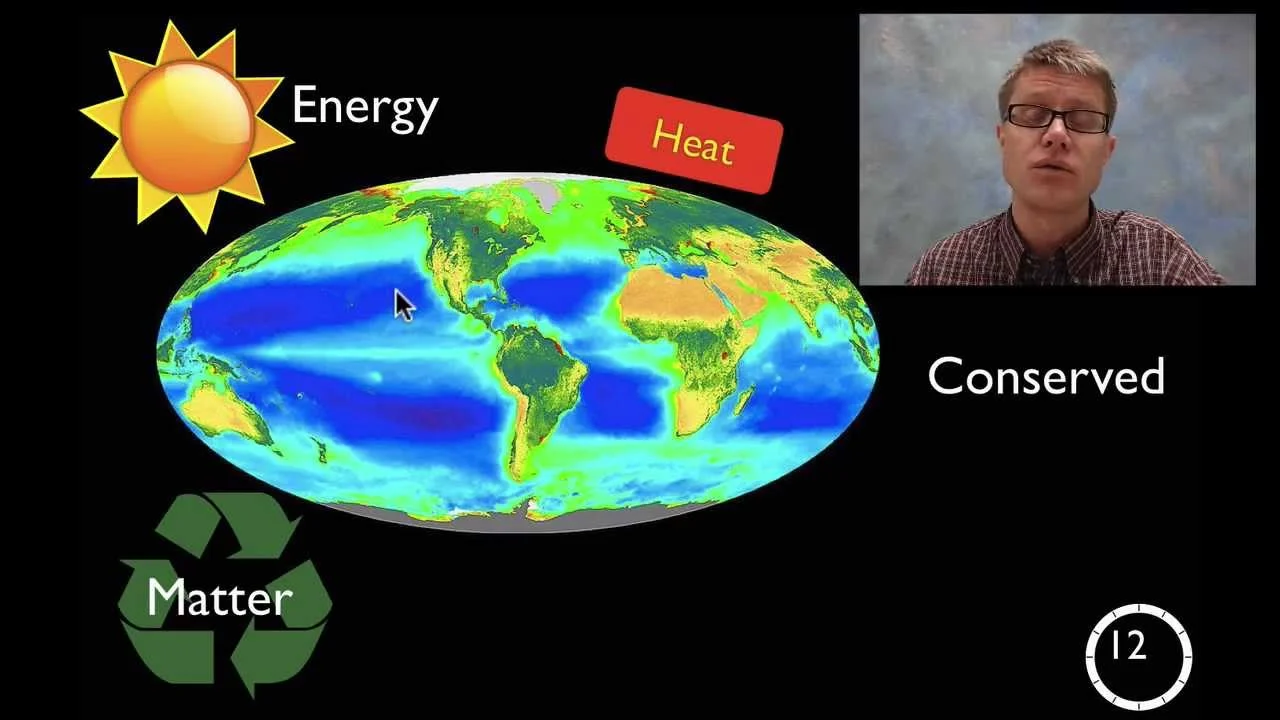
LS1.C: Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms
Sustaining life requires substantial energy and matter inputs. The complex struc- tural organization of organisms accommodates the capture, transformation, trans- port, release, and elimination of the matter and energy needed to sustain them.
As matter and energy flow through different organizational levels—cells, tissues, organs, organisms, populations, communities, and ecosystems—of living systems, chemical elements are recombined in different ways to form different products. The result of these chemical reactions is that energy is transferred from one system of interacting molecules to another.
LS1.B: Growth and Development of Organisms
Paul Andersen answers the following question:
How do organisms grow and develop?
LS1.A: Structure and Function
How do the structures of organisms enable life's functions? Benchmarks for grades 2, 5, 8 and 12 are included.
ETS1.B: Developing Possible Solutions
In this video Paul Andersen explains how many possible solutions are developed in the design process. As many solutions to the problem are identified using a brainstorming process. These solutions are compared to the specific constraints and criteria of the solution. Models are created to test the viability of each solution. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.
ESS3.D: Global Climate Change
In this video Paul Andersen explains how humans are impacting the Earth through farming, mining, pollution and climate change. According to the NGSS wise management can reduce impacts on the planet. This will become more important as developing countries start consuming more resources. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.
ESS3.C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
In this video Paul Andersen explains how humans are impacting the Earth through farming, mining, pollution and climate change. According to the NGSS wise management can reduce impacts on the planet. This will become more important as developing countries start consuming more resources. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.
ESS3.B: Natural Hazards
In this video Paul Andersen explains how natural disasters (like earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes and flooding) have affected and will continue to affect humans on the planet. Many of the natural hazards (like volcanoes and storms) can be studies directly and some (like earthquakes) can be predicted. Natural hazards will never go away but the damage can be limited. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.
ESS3.A: Natural Resources
In this video Paul Andersen explains how the resources required for survival come from the Earth. The resources are not evenly distributed on the planet and neither are the humans. According to the NGSS we need to limit the use of nonrenewable resources (like oil and coal) through regulations and increase the use of renewable resources. A teaching progression K-12 is also included.
ESS2.E: Biogeology
In this video Paul Andersen explains the topic of biogeology. Life only exists where the geosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere allow life to exist. The interactions between the organisms on the planet and the planet itself is known as biogeology. As the landforms on the planet change the lifeforms adapt through evolution. The biosphere can also impact the Earth itself. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.
ESS2.D: Weather and Climate
In this video Paul Andersen describes both weather and climate. Weather is the day-to-day conditions on the Earth's surface, including temperature, wind, humidity, air pressure, and precipitation. Climate are the long term conditions on the Earth's surface. Both climate and weather are determined by sunlight, water, landforms and life forms. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.
ESS2.C: The Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes
In this video Paul Andersen explains the vital role that water plays in the processes on the Earth's surface. Water has several unique properties including high heat capacity, transparency, polarity and the ability to change the chemical behavior of the mantle. The Earth is largely a water planet but most of the water is found in the oceans or locked in ice. Water is a powerful erosive force on the planet. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.
ESS2.B: Plate Tectonics and Large-Scale System Interactions
In this video Paul Andersen explains how plate tectonics explains the large-scale system interactions on our planet. Large plates float on the mantle and interact to form the major landforms on the planet. Evidence for plate tectonics include the location of earthquakes, the reversed polarity of newly formed oceanic crust and the warping of crust by large bodies like glaciers and lakes. A K-12 teaching progression is also included.