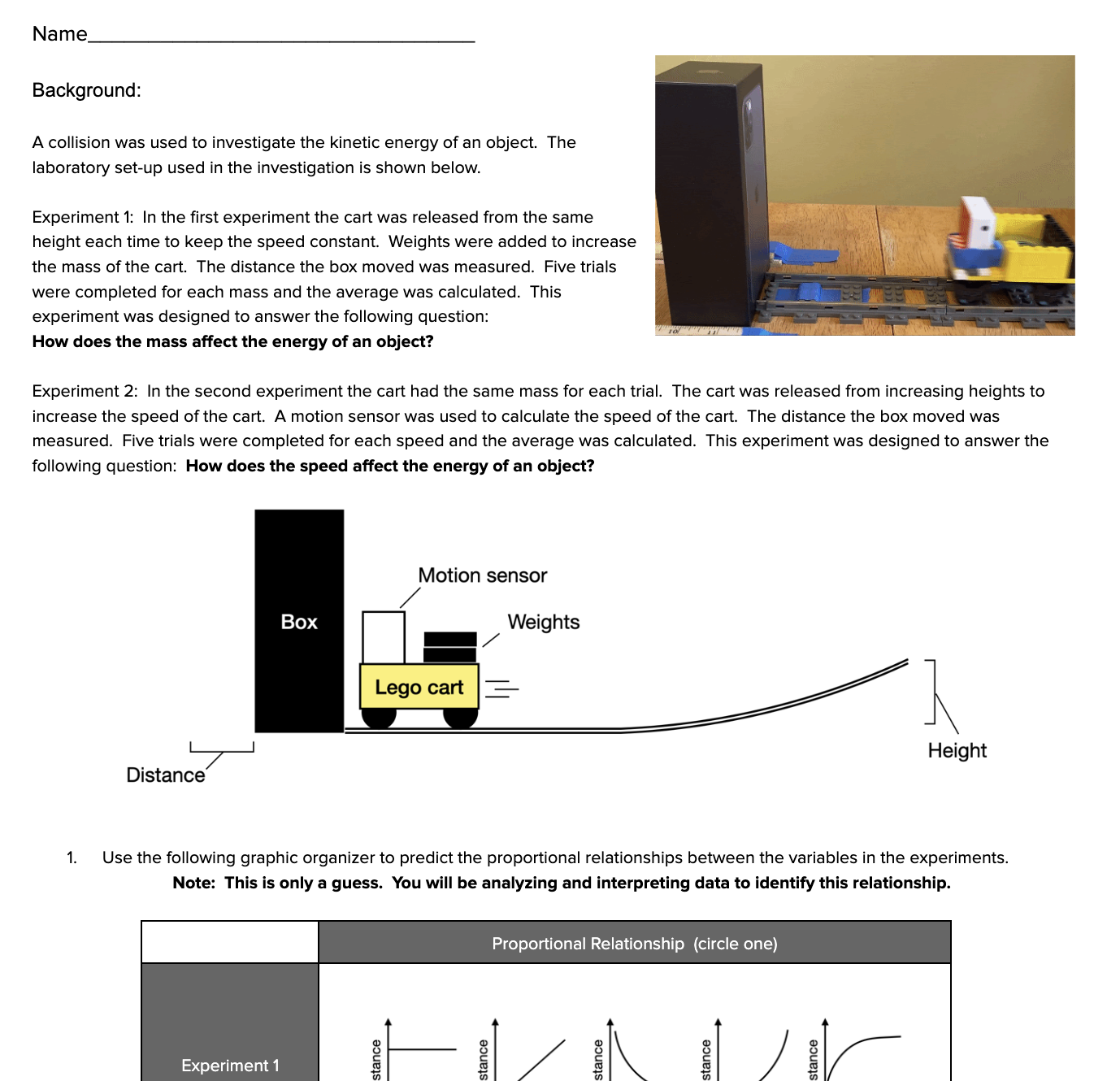
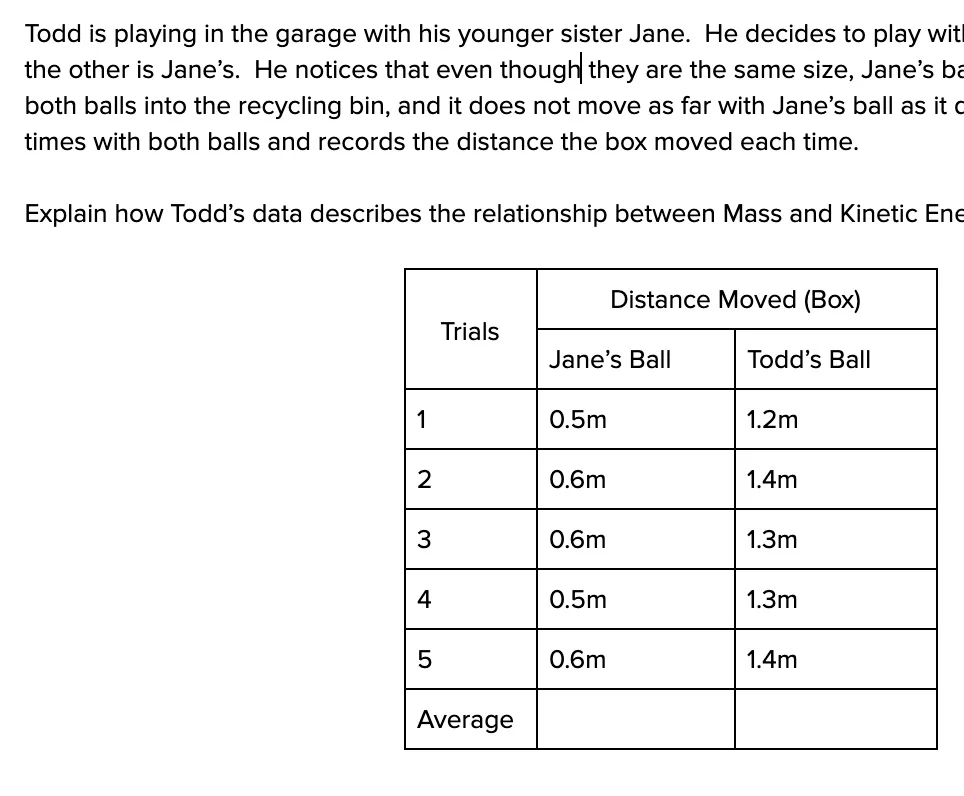
MS-PS3-1: Kinetic Energy of an Object
Construct and interpret graphical displays of data to describe the relationships of kinetic energy to the mass of an object and to the speed of an object. (Scale, Proportion, and Quantity)
Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on descriptive relationships between kinetic energy and mass separately from kinetic energy and speed. Examples could include riding a bicycle at different speeds, rolling different sizes of rocks downhill, and getting hit by a wiffle ball versus a tennis ball.
Assessment Boundary: none
Science Practices
Analyzing and Interpreting Data
Disciplinary Core Ideas
PS3.A: Definitions of Energy
Crosscutting Concepts
Scale, Proportion, and Quantity
Assessments
The Wonder of Science Assessments
Shared Assessments
The following assessments were created by science teachers hoping to better understand the NGSS. In most cases teachers went from standard to assessment in around an hour. These are drafts and should be used accordingly. Feel free to improve these assessments or contribute to the collection. Learn more about assessment design here.
Instructional Resources
Mini Lessons
The Wonder of Science Resources
Anchor Charts
Phenomena
Videos
Learning Plans
Storylines
Common Core Connections
ELA/Literacy
RST.6-8.1 - Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts.
RST.6-8.7 - Integrate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text with a version of that information expressed visually (e.g., in a flowchart, diagram, model, graph, or table).
Mathematics
6.RP.A.1 - Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities. (MS-PS3-1)
6.RP.A.2 - Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b ≠0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship.
7.RP.A.2 - Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities.
8.EE.A.1 - Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions.
8.EE.A.2 - Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x² = p and x³ = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational.
8.F.A.3 - Interpret the equation y = mx + b as defining a linear function, whose graph is a straight line; give examples of functions that are not linear.
MP.2 - Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
*Next Generation Science Standards is a registered trademark of Achieve. Neither Achieve nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it. Visit the official NGSS website.